Study Guide: Doppler Effect

- The Doppler Effect is an apparent shift in frequency (or tone) for listeners of sound from a moving source.
- The Doppler Effect occurs in all forms of waves, including sound and light.
Doppler Effect
The Doppler effect is heard whenever a source of sound waves is moving with respect to an observer.
There is an apparent upward shift in frequency (or tone) for observers towards whom the source is approaching and an apparent downward shift in frequency (or tone) for observers from whom the source is receding.
It is important to remember that this is not because of an actual change in the frequency of the source.
The Doppler effect can be observed for any type of wave - water wave, sound wave, light wave, etc. We are most familiar with the Doppler effect of sound waves because our ears are well-tuned to hear certain frequencies of sound waves.
The Doppler Effect in Astronomy
The Doppler effect is of intense interest to astronomers who use the information about the shift in frequency of electromagnetic waves produced by moving stars in our galaxy and beyond to derive information about those stars and galaxies.
The theory that the universe is expanding is based in part on observations of electromagnetic waves emitted by stars in distant galaxies. Electromagnetic radiation emitted by stars in a distant galaxy appears to shift downward in frequency (a red shift) if the star is moving away from the Earth. There is an upward shift in frequency (a blue shift) for stars that move towards the Earth.
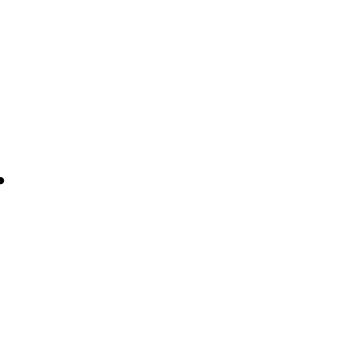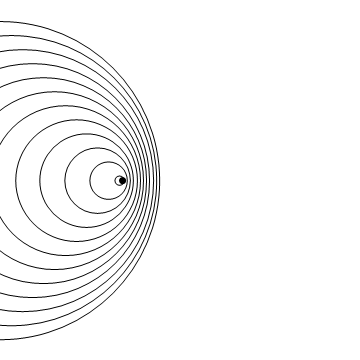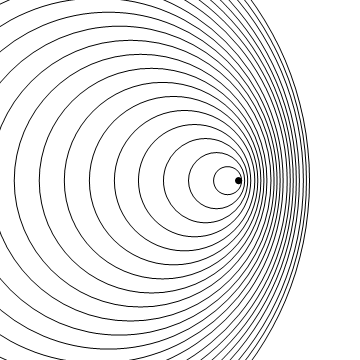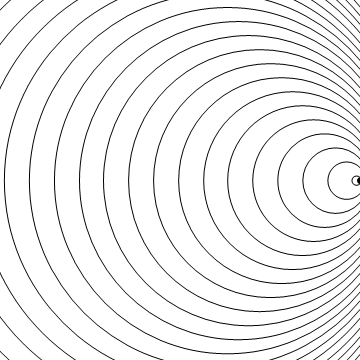
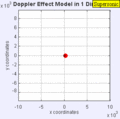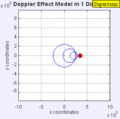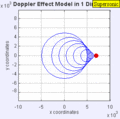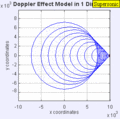
Stationary Object
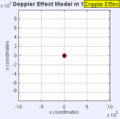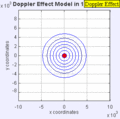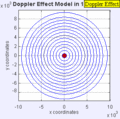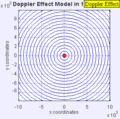
Moving to the Right at MACH 0.7
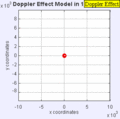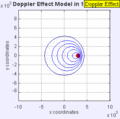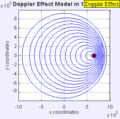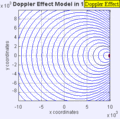
Moving to the Right at MACH 1 (Speed of Sound)
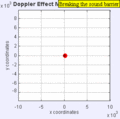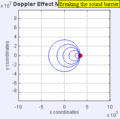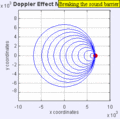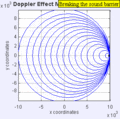
Moving to the Right at MACH 1.4
Moving to the Right at MACH 5
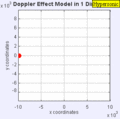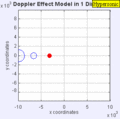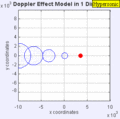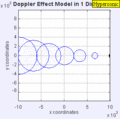
Demonstrations
- Fast, loud vehicles passing by
- Spinning object
- Try to record the change in tone.


