Study Guide: Levers
Vocabulary
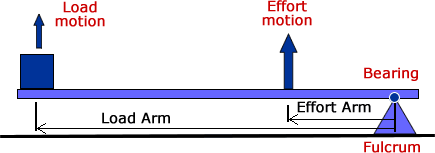
- Lever: A bar or pole resting on a pivot, used to help move a heavy load.
- Fulcrum: The point on which a lever pivots.
- Load: The weight or object moved by a lever.
- Effort (or Force): The work done to move a load with a lever.
The Three Types of Levers
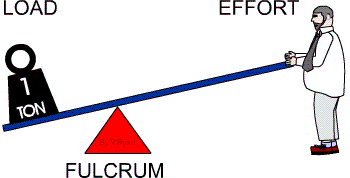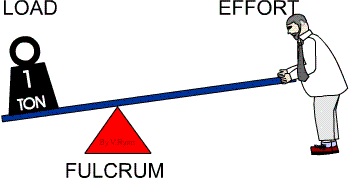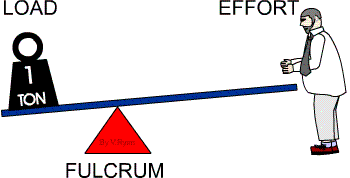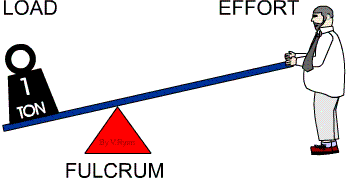
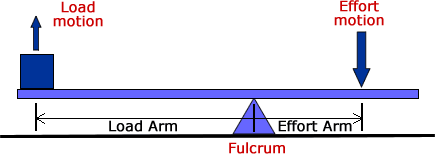
- Class 1 Levers: The Fulcrum is in the middle.
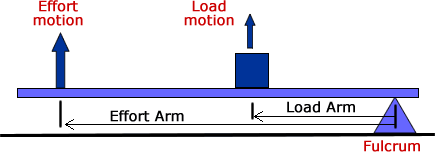
- Class 2 Levers: The Load is in the middle.
- Class 3 Levers: The Effort is in the middle.
- Memorize: “123 FLE”
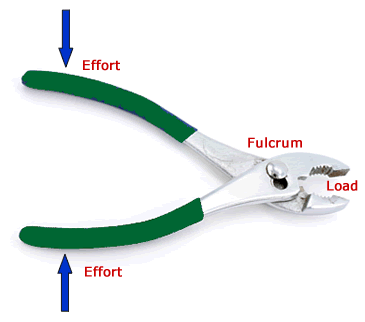
Class 1 Levers
A Class 1 lever has the fulcrum between the effort and load. The movement of the load is in the opposite direction of the movement of the effort. This is the most common lever. Examples of class 1 levers include:
- Teeter-totter
- Oars on a rowboat
- Catapult
- Shoehorn
- Scissors (Double Class 1 lever)
- Pair of pliers (Double Class 1 lever)
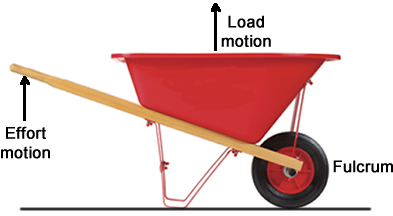
Class 2 Levers
A Class 2 lever has the load between the effort and the fulcrum. In this type of lever, the movement of the load is in the same direction as the effort. Examples of Class 2 levers include:
- Wheelbarrow
- Crowbar
- Nutcracker
Class 3 Levers
A Class 3 lever has the effort between the load and the fulcrum. Both the effort and load are in the same direction. Examples of Class 3 levers include:
- Tweezers
- Stapler
- Mousetrap
- Broom
- Hockey stick
The Law of the Lever
The cross product of force and distance equals torque.
$$ F_1 \times d_1 = F_2 \times d_2 $$- F1 is Force 1.
- d1 is the distance from the fulcrum to Force 1.
- F2 is Force 2.
- d2 is the distance from the fulcrum to Force 2.
Example of the Law of Levers
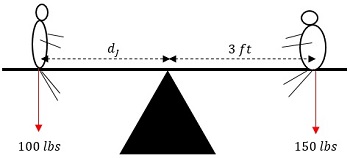
Bill weighs 150 pounds. Jenny weighs 100 pounds. Bill sits on a seesaw 3 feet from the fulcrum. How far away from the fulcrum on the other end of the seesaw does Joe need to sit to balance the seesaw, i.e., keep it in equilibrium)?
\begin{aligned} F_j \times d_j &= F_b \times d_b \\\ 100 \times d_j &= 150 \times 3 \\\ d_j &= \dfrac{450 }{100} \\\ d_j &= 4.5 \text{ feet} \end{aligned}
- Fb = Bill’s weight (150 lb).
- Fj = Jenny’s weight (100 lb).
- db = the distance Bill sits from the fulcrum (3 feet).
- dj = the distance Jenny must sit from the fulcrum.