Study Guide: Islamic Mosaic Art
Islam is a religion based on the holy book, the Qur’an (sometimes spelt Koran), which followers believe to be the word of Allah (God) as revealed through the Archangel Gabriel to the Prophet Mohammed in the early 7th century. Followers of Islam are called Muslims.
The Prophet Mohammed was born in Arabia around 571 CE and died in 632 CE. Within 100 years, Islam had spread westward as far as Spain and eastward to the Indus Valley. It continued to expand into Turkey, and deeper into the India, into north-western China and South-East Asia.
As the Islamic culture spread, it adopted traditions and knowledge from local environments. Islamic art is influenced by Arabic, Persian, Mesopotamian, African and Byzantine traditions. Yet Islamic art is also unique in its own way.
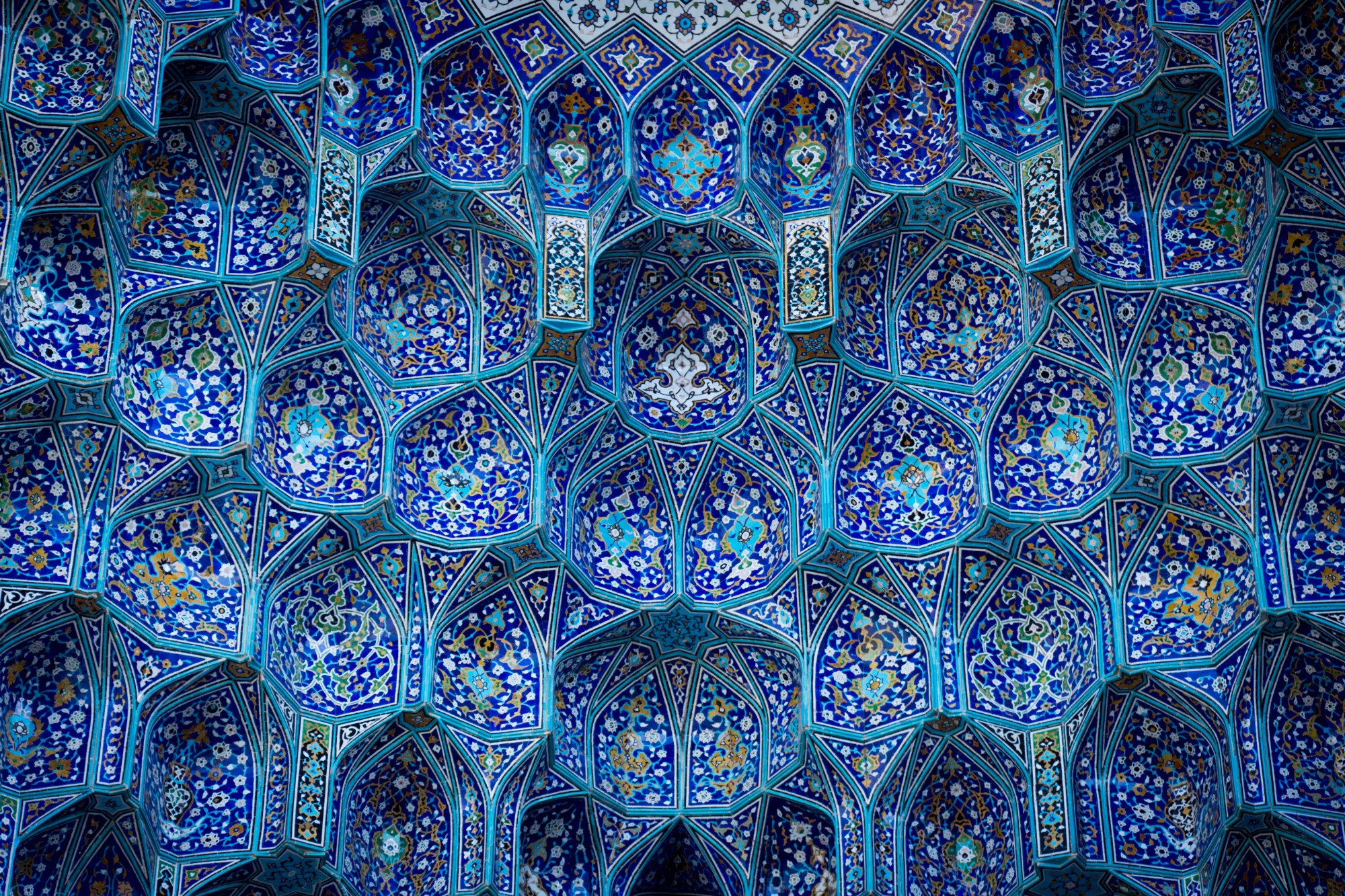
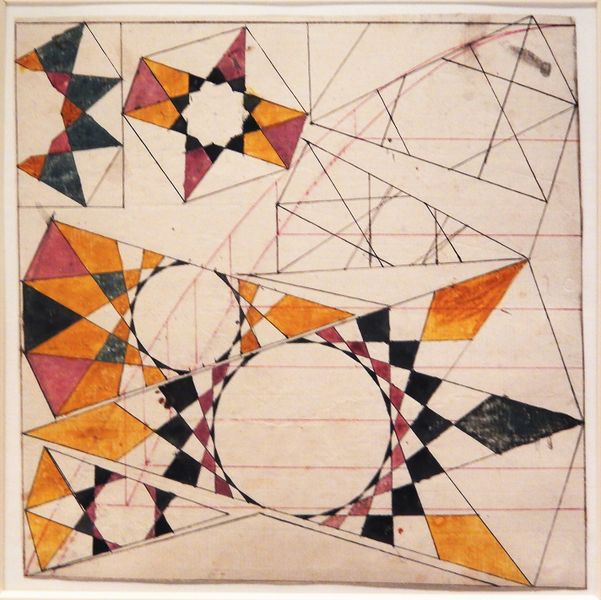
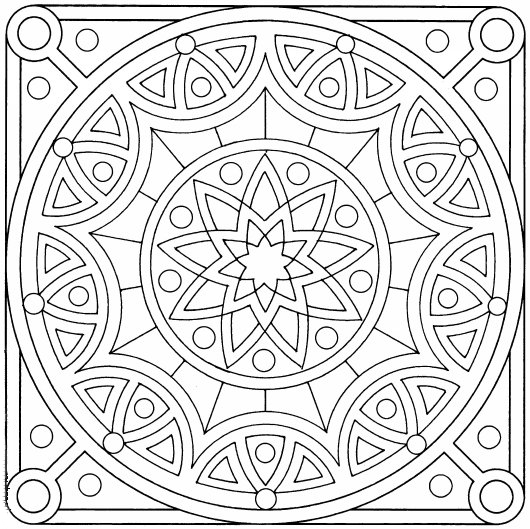
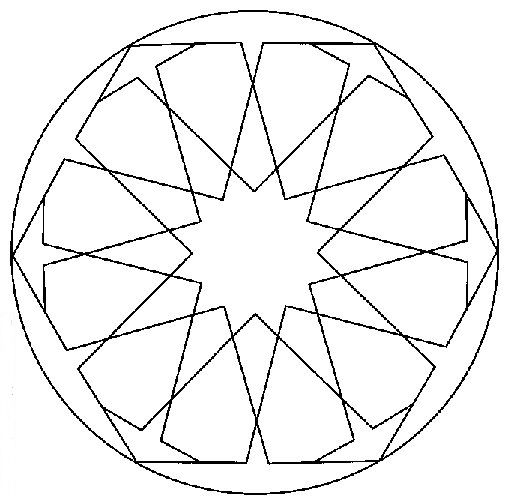
In Islam, the tradition is to not depict living creatures, as this is associated with idolatry (following false gods). Abstract geometrical patterns were favored. They were based on mathematical shapes and forms because it was felt that this encouraged spiritual contemplation.
- Circles have no end—they are infinite—and so they remind Muslims that Allah (God) is infinite.
- Complex geometric designs create the impression of unending repetition, and this get a feeling for the infinite nature of Allah (God).
- Repeating patterns represent that even the smallest details are part of the infinite.
- Symmetry illustrates Allah’s love of beauty.
Shapes
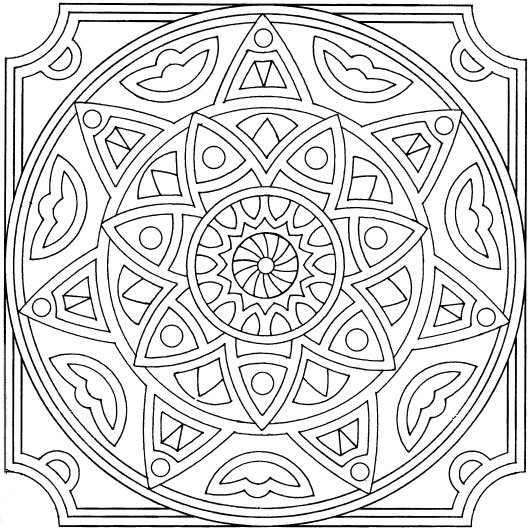
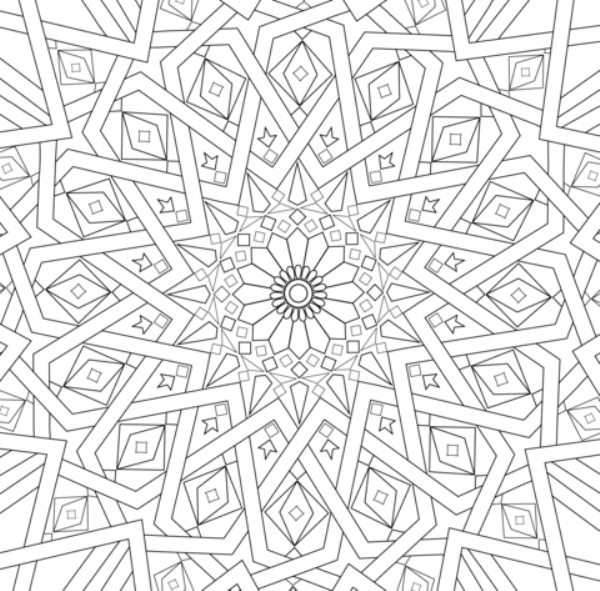
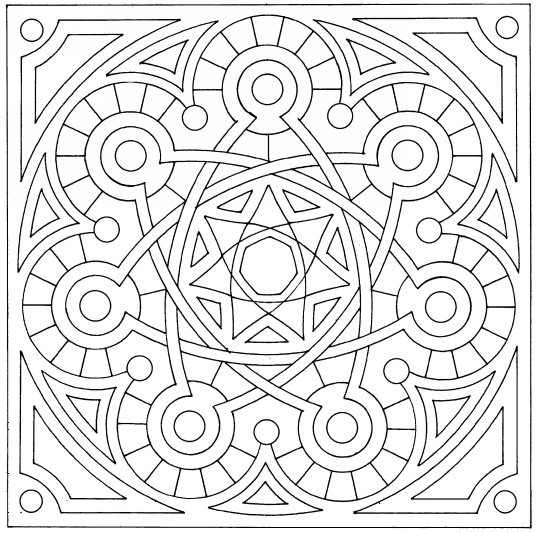
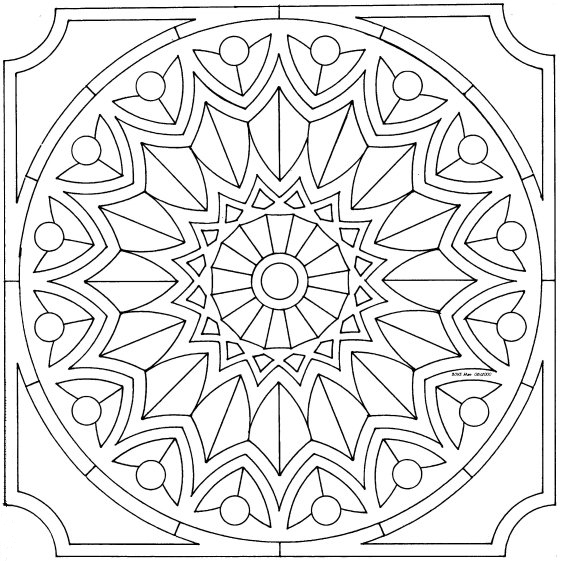
Islamic geometric patterns were one of the first forms of art in the Arabian Peninsula. Islamic art features geometric designs, using squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles. Circles represent how Allah (God) is infinite.
Colors
Traditional colors often see in Islamic designs are shades of blue and gold.
Symmetry?
Symmetry is a similarity—or balance—between different parts of a design.
Linear Symmetry
Imagine a line draw down the center of a geometric pattern. If both sides balanced then the design has linear symmetry—also called mirror or lateral symmetry.
Radial Symmetry
Radial (or rotational) symmetry is symmetry around a central point.
Repeating Patterns
Repeating patterns symbolize how each element is part of a universal whole. Just as one tiny triangle is part of a larger pattern, each person is part of the universe. Patterns may repeat along a line, or within a shape.
Calligraphy
The Islamic world took writing to a high art, and their script is one of the most beautiful.
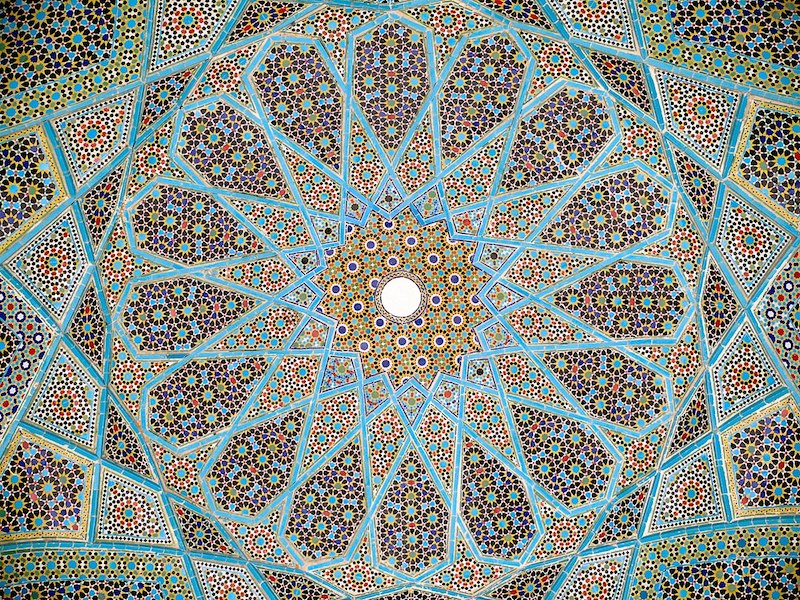

Iranian glazed ceramic tile work, from the ceiling of the Tomb of Hafez in Shiraz, Iran. CC Photo credit: Pentocelo
Sources
- https://kids.kiddle.co/Islamic_geometric_patterns
- https://kidworldcitizen.org/islamic-art-lesson-for-kids/
- https://artofislamicpattern.com/resources/educational-posters/